Related
100% Open-Source Self-Hostable AI Code Editing: Codium & Continue.dev
A comprehensive guide to setting up fully self-hosted AI code editing with Codium and Continue.dev, keeping your code and AI interactions...
Popular topics
02 min reading in—DevOpsMonitoring
Tiny guide to deploy Uptime-Kuma on a self-hosted Kubernetes cluster using a maintained Helm chart.
Uptime-Kuma is a lightweight status and monitoring dashboard suited for homelabs or lean production clusters. Below is a minimal, repeatable setup to run it behind an ingress with TLS.
A maintained chart is available: dirsigler/uptime-kuma-helm, from @dirsigler.
helm repo add uptime-kuma https://helm.irsigler.cloud
helm repo update
helm upgrade my-uptime-kuma uptime-kuma/uptime-kuma \
--install \
--namespace monitoring \
--create-namespace \
-f values.uptime-kuma.yaml
The following screenshot shows how Uptime-Kuma presents monitoring data for this blog (blog.t1m.me).
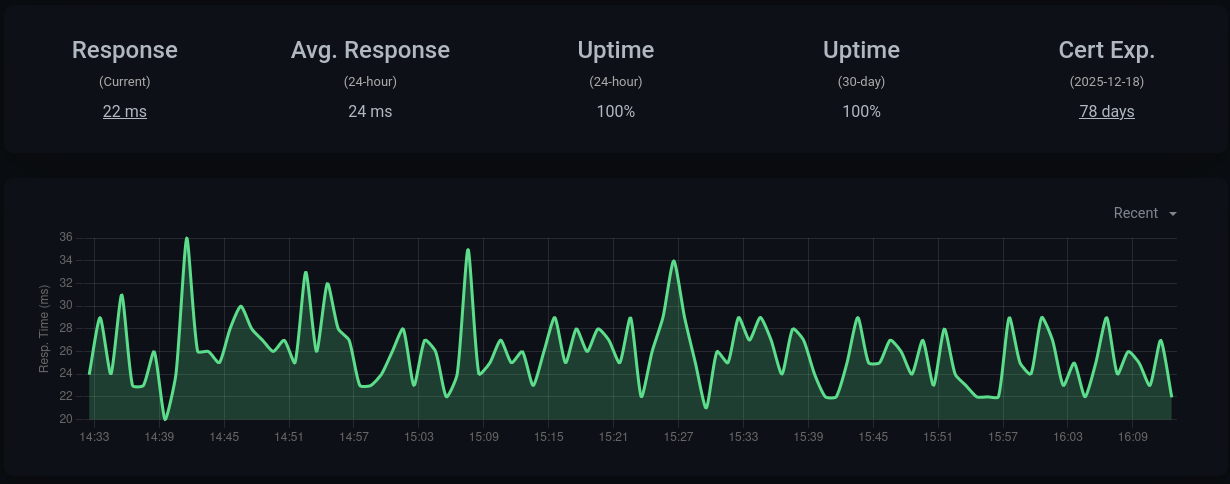
Sanitize hosts/secrets for the target environment. This example runs as a ClusterIP behind nginx and cert-manager.
ingress:
enabled: true
ingressClassName: public
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-prod
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: public
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/enable-cors: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-origin: "https://<your-domain>"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-methods: "GET, OPTIONS"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-headers: "Content-Type"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/cors-allow-credentials: "false"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-read-timeout: "3600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-send-timeout: "3600"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/server-snippets: |
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_cache off;
hosts:
- host: status.<your-domain>
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- secretName: uptime-kuma-tls
hosts:
- status.<your-domain>
persistence:
enabled: true
size: 5Gi
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 3001
env:
TZ: Europe/Berlin
A helper script is available for quick install and values generation:
setup_uptime_kuma.shcurl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tbscode/tims-blog-posts/refs/heads/main/assets/setup_uptime_kuma.sh -o setup_uptime_kuma.sh
chmod +x setup_uptime_kuma.sh
KUBECONFIG=./kubeconfig.yaml HOST="status.<your-domain>" ./setup_uptime_kuma.sh
Notes:
ingress and cert-manager are enabled and a ClusterIssuer named letsencrypt-prod exists.https://status.<your-domain> after DNS is set.That’s it—small, stable, and easy to back up. Perfect for keeping a quiet eye on your stack.
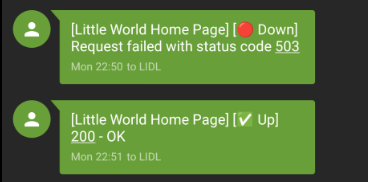
/app/data and keeping a sensible retention schedule is recommended.Related
A comprehensive guide to setting up fully self-hosted AI code editing with Codium and Continue.dev, keeping your code and AI interactions...
Related
How to self host a Matrix.org server
Related
How Open-Chats Federation Enables anybody to host anything anywhere